What is the difference between milling and cnc turning? Learn the key differences.

In the engineering industry, both milling and turning are key processes for machining materials. Although both techniques are used to shape metal, plastic or wooden parts, they differ in their operating principle, applications and end results. In this article, we will take a closer look at these two methods to understand how they differ and in which situations they are used.
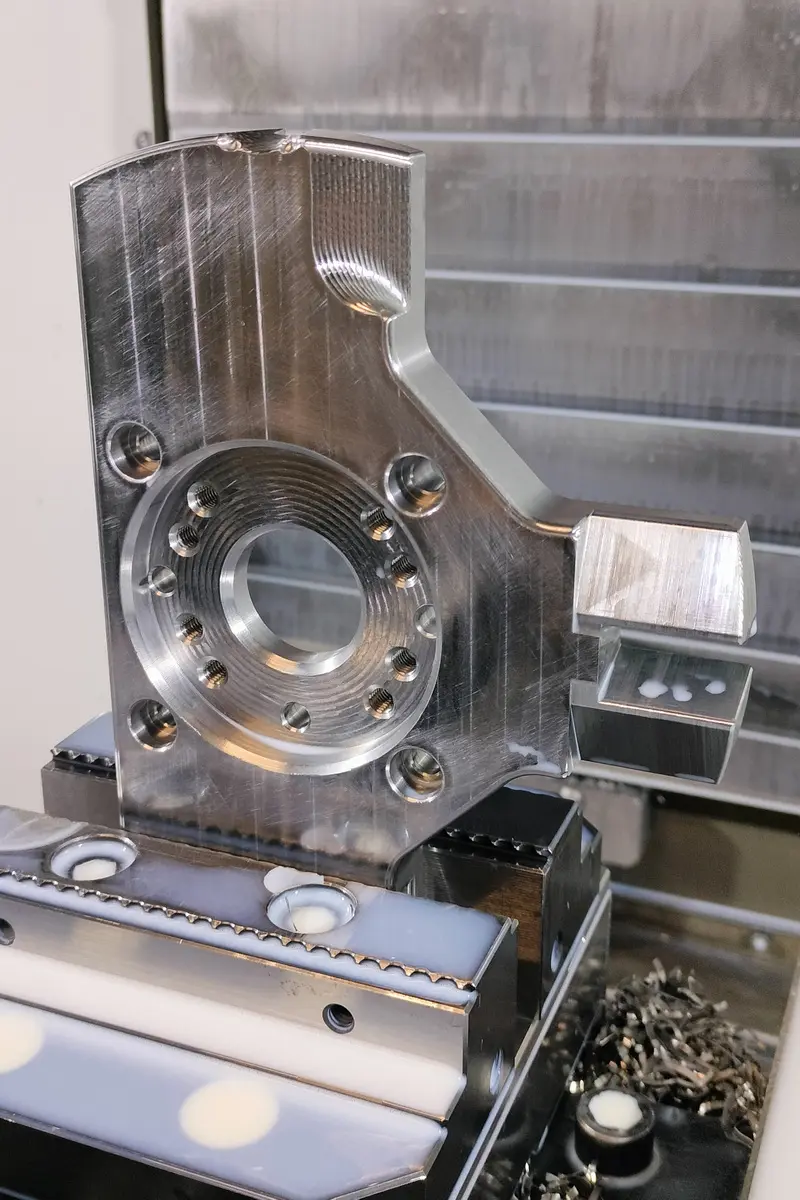
Milling – what does it involve?
Milling is a machining process in which the tool (cutter) rotates and the workpiece is usually stationary or moves relative to the tool. The milling cutter can move in different directions to create intricate shapes, grooves, holes or protrusions. This process is often used to produce parts with complex geometries, such as machine bodies, injection moulds or mechanical parts.
Main features of milling:
Tool movement – The cutter rotates while the workpiece is stationary or moves linearly.
Multi-axis – Modern CNC milling machines can operate in 3, 4 or even 5 axes to create very complex shapes.
Materials – Milling can be used for metals, plastics, wood and composites.
Applications – Making precision detail with complex shapes.
Turning – what does it involve?
Turning is a machining process in which the workpiece (mounted in a lathe chuck) rotates and the lathe tool moves linearly to remove material. Turning is ideal for producing cylindrical, conical or spherical workpieces such as shafts, bushings, screws or rings.
Key rolling features:
Workpiece movement: The workpiece rotates and the turning tool moves linearly.
Axiality: Turning usually takes place in one or two axes.
Materials: Turning is mainly used for metals, but can also be used for plastics and wood.
Applications: The manufacture of symmetrical components such as shafts, bushings, fittings, bolts and other cylindrical components.
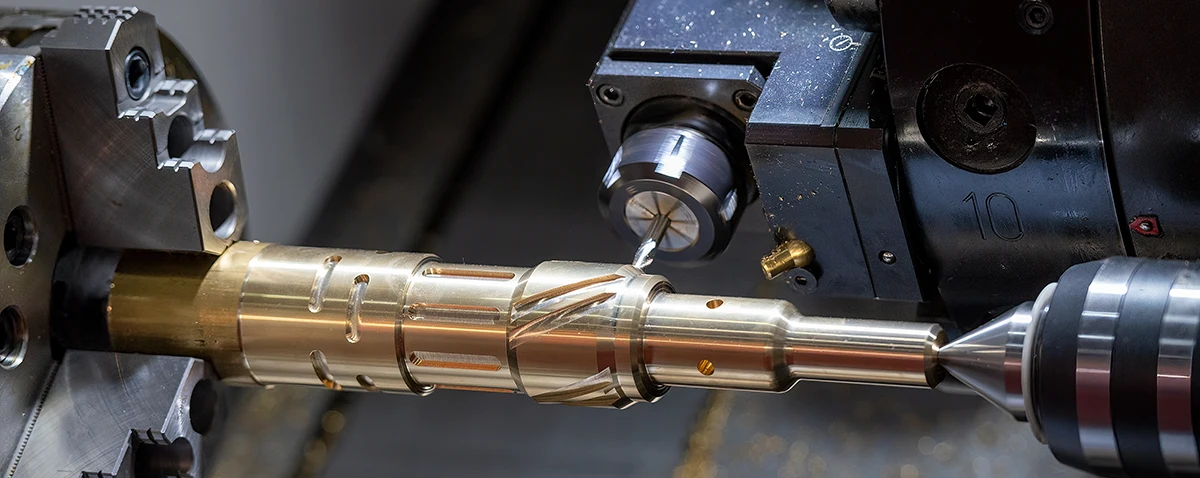

Basic differences between milling and turning
1. Operating principle
- Milling: the tool (cutter) rotates while the workpiece is stationary or moves linearly.
- Turning: The workpiece rotates and the turning tool moves linearly.
2. Shape of workpieces
- Milling: Ideal for creating complex shapes, grooves, pockets and 3D surfaces.
- Turning: Used mainly for symmetrical components such as shafts, bushings or cones.
3. Precision and capability
- Milling: thanks to multi-axis CNC machines, milling offers greater flexibility in creating complex geometries.
- Turning: Turning is more limited in terms of shaping possibilities, but provides high precision for cylindrical parts.
4. Industrial applications
- Milling: Often used in the manufacture of injection moulds, machine bodies, mechanical components with complex shapes.
- Turning: Mainly used for machine parts such as shafts, bushings, rings, bolts, pins, etc.
5. Types of machinery
- Milling: CNC 3-, 4- and 5-axis milling machines, vertical milling machines, horizontal milling machines.
- Turning: 2-axis CNC lathes, multi-axis lathes (3-, 4- and 5-axis), vertical lathes, horizontal lathes, turning and milling centres.
When to choose milling and when to choose turning?
The choice between milling and turning depends on several factors:
- Shape of the component: If you need symmetrical components (e.g. shafts), choose turning. If you need complex shapes (e.g. bodies, plates), milling is better.
- Material: Both methods can machine similar materials, but some materials are better suited to turning and others to milling.
- Precision: both methods offer high precision, but milling is more flexible for complex parts.
- Cost: Turning can be cheaper for simple components, while milling is more cost-effective for complex projects.
Summary
Milling and turning are two different but complementary machining techniques. Milling is ideal for creating complex shapes and details, while turning works well for producing symmetrical parts. Choosing the right method depends on the type of project, the material and the precision and cost requirements. In modern industry, both techniques are often combined to achieve optimum results.
If you are wondering which method is best for your project, please contact us. We will be happy to advise you and answer all your questions.




